【Zookeeper】Curator-分布式锁的实现 介绍了`Curator`如何实现的mutex,那么它也有读写锁的实现,废话不多说,先看它的设计.
那么它做了以下的改造完成了读写锁实现.
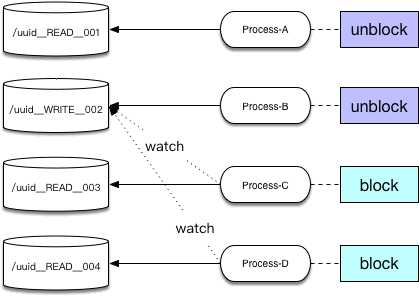
读锁节点为uuid__READ__sequence,写锁为uuid__WRIT__sequence
读锁、写锁分别是一个InterProcessMutex的子类
是否可读判断依据为排序后的节点,从当前线程写入节点的所有前置节点中没有__WRIT__的节点
是否可写的判断依据当前线程节点前没有其他__WRIT__节点
下面针对代码来快速的看一遍.
Common 1 2 3 private static final String READ_LOCK_NAME = "__READ__" ;private static final String WRITE_LOCK_NAME = "__WRIT__" ;
定义了读写锁节点Path中段标识.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 private static class InternalInterProcessMutex extends InterProcessMutex private final String lockName; private final byte [] lockData; InternalInterProcessMutex(CuratorFramework client, String path, String lockName, byte [] lockData, int maxLeases, LockInternalsDriver driver) { super (client, path, lockName, maxLeases, driver); this .lockName = lockName; this .lockData = lockData; } @Override public Collection<String> getParticipantNodes () throws Exception { Collection<String> nodes = super .getParticipantNodes(); Iterable<String> filtered = Iterables.filter ( nodes, new Predicate<String>() { @Override public boolean apply (String node) { return node.contains(lockName); } } ); return ImmutableList.copyOf(filtered); } @Override protected byte [] getLockNodeBytes() { return lockData; } }
创建了InterProcessMutex的一个子类,对读写锁进行了一个抽象,重写了getParticipantNodes()方法使其返回相同类型的节点数据,判断依据就是节点中是否包含相应锁的中段标识.
writeLock 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 writeMutex = new InternalInterProcessMutex ( client, basePath, WRITE_LOCK_NAME, lockData, 1 , new SortingLockInternalsDriver() { @Override public PredicateResults getsTheLock (CuratorFramework client, List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName, int maxLeases) throws Exception { return super .getsTheLock(client, children, sequenceNodeName, maxLeases); } } );
writeLock就是一个InterProcessMutex,也就是独占锁,writeLock写的节点前没有其他writeLock,那就是获得锁.
readLock 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 readMutex = new InternalInterProcessMutex ( client, basePath, READ_LOCK_NAME, lockData, Integer.MAX_VALUE, new SortingLockInternalsDriver() { @Override public PredicateResults getsTheLock (CuratorFramework client, List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName, int maxLeases) throws Exception { return readLockPredicate(children, sequenceNodeName); } } );
readLock稍微有所不同,readLock是一个共享锁,在构造InternalInterProcessMutex上传入了一个Integer.MAX_VALUE值,也就是说只要节点中的read节点不超过Integer.MAX_VALUE那么都可以获得锁(前提是没有write锁).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 private PredicateResults readLockPredicate (List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName) throws Exception if ( writeMutex.isOwnedByCurrentThread() ) { return new PredicateResults(null , true ); } int index = 0 ; int firstWriteIndex = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int ourIndex = -1 ; for ( String node : children ) { if ( node.contains(WRITE_LOCK_NAME) ) { firstWriteIndex = Math.min(index, firstWriteIndex); } else if ( node.startsWith(sequenceNodeName) ) { ourIndex = index; break ; } ++index; } StandardLockInternalsDriver.validateOurIndex(sequenceNodeName, ourIndex); boolean getsTheLock = (ourIndex < firstWriteIndex); String pathToWatch = getsTheLock ? null : children.get(firstWriteIndex); return new PredicateResults(pathToWatch, getsTheLock); }
总结 Curator读写锁实现比较简单而且巧妙,使用起来注意以下几点.
写锁可以降级为读锁,但是读锁不能升级为写锁.
读写锁都可重入,但在有写锁的时候,读锁是不可进行重入的,直到写锁释放后才可以重入.
写锁是公平锁.